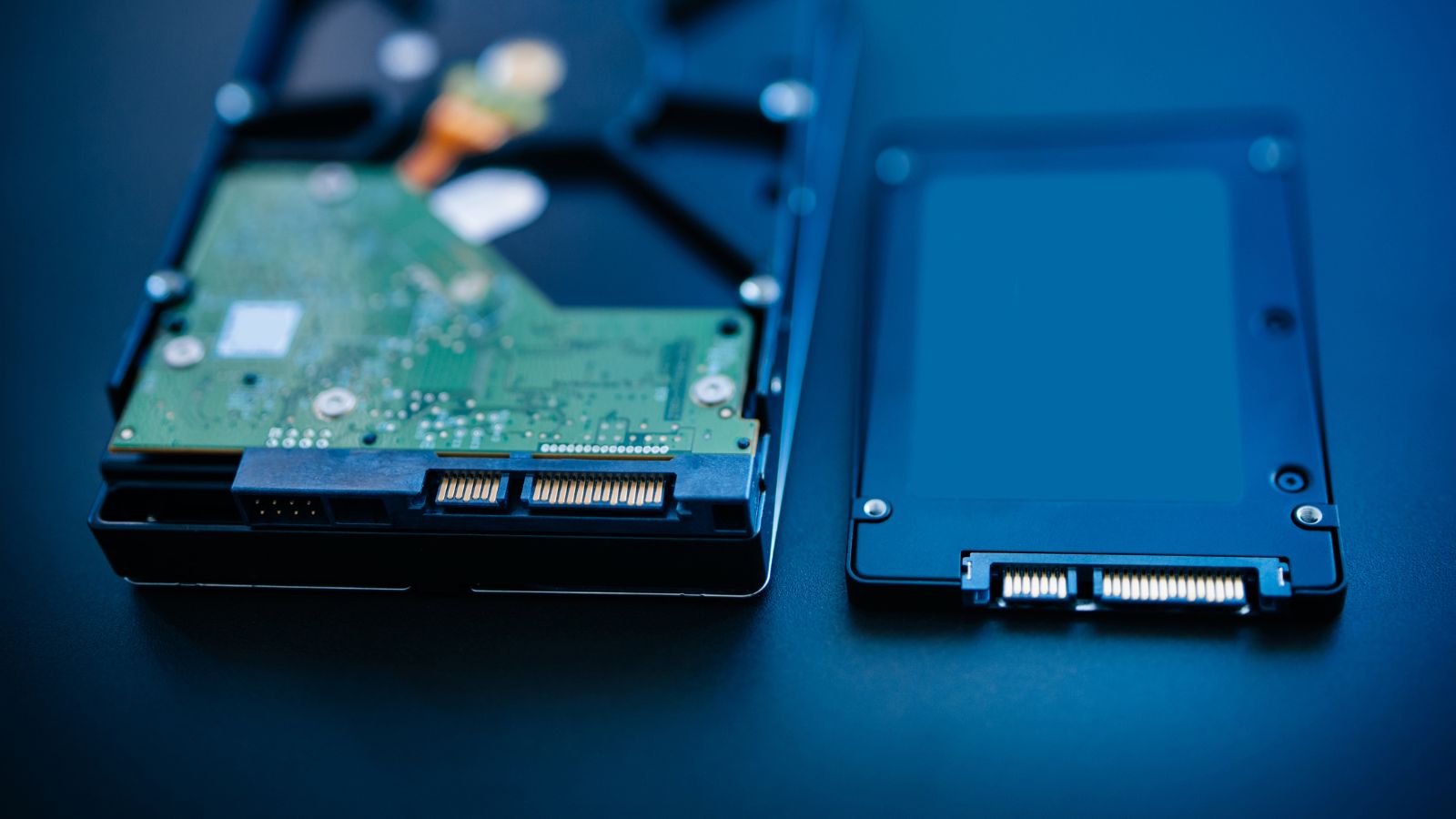
HDD vs SSD – Everything you need to know about PC Storage
HDD vs SSD – although nowadays fairly easy choice (for most of us), but that was not the case a few years back. Solid state drives (SSDs) and hard disk drives (HDDs) may seem similar in their physical specifications, but they fundamentally differ in how they store data. Choosing between HDD vs SSD storage options depends on how you use your computer.

As part of these comprehensive guides on PC Components, in this Blog, we’ll delve into the inner workings of each storage type and tell you Everything you need to know about PC Storage.
How HDDs Work?
HDDs are composed of one or more magnetically sensitive platters, an actuator arm equipped with a read/write head for each platter, and a motor to spin the platters and move the arms. Additionally, there is an I/O controller and firmware that coordinates the hardware’s functions and communicates with the rest of the system.

These platters are organized into concentric circles called tracks, with each track divided into logical units called sectors. Each track and sector combination creates a unique address for data organization and retrieval. Before writing data, an algorithm processes it, allowing the firmware to detect and correct errors. The platters spin at preset speeds, which correlate with read/write rates.

Reading and Writing on HDDs
When you request your computer to access or update data, the I/O controller instructs the actuator arm to locate the data’s position, and the read/write head retrieves the data by reading the presence or absence of a charge at each address. If the request is for data updating, the read/write head changes the charge on the relevant track and sector. The time it takes for the platter to spin, and the actuator arm to find the correct track and sector is known as latency.
Drawbacks of HDDs
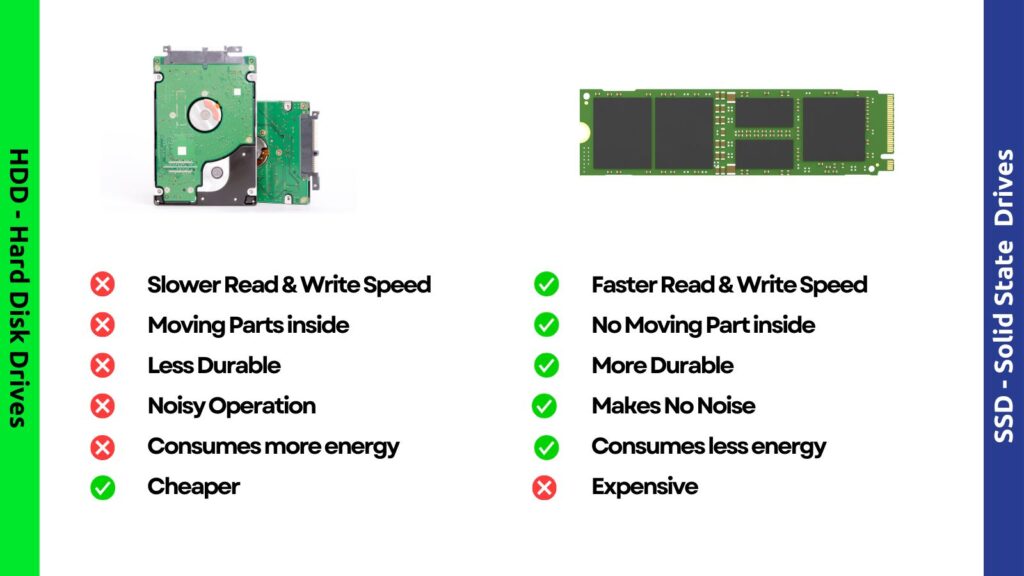
HDDs have drawbacks primarily due to their mechanical parts used for data retrieval. Physically finding and retrieving data takes more time than electronically accessing it. The mechanical parts can skip or even fail if handled roughly or dropped, particularly concerning laptops. Additionally, HDDs are heavier and consume more energy compared to their SSD counterparts.
Benefits of HDDs
On the positive side, HDDs are a well-proven technology and are often more cost-effective than SSDs when it comes to storage capacity. Currently, HDDs offer higher storage capacities compared to SSDs.

What is an SSD?
Solid-state drives (SSDs) utilize flash memory to offer superior performance and durability. Unlike HDDs with multiple moving parts, including magnetic heads, spindles, and spinning platters, SSDs lack moving components, making them more reliable, resistant to wear, and energy-efficient.

How SSDs Work
SSDs can be likened to large USB drives, utilizing the same base technology. They store data using NAND flash memory technology, which operates significantly faster than traditional hard disks. SSDs contain no moving parts, making them more resilient.
The core component of NAND-based SSDs is the floating gate transistors that store data through the presence or absence of a charge. These gates are organized into a grid pattern, forming blocks. An SSD controller manages data locations and operations.
Reading and Writing on SSDs
Updating data on SSDs is a bit more intricate. When any part of a block is updated, the entire block must be refreshed. The data from the old block is copied to a different block, and the old block is erased before rewriting the data with the changes. The SSD controller reads the charge status when you request data retrieval or updates.
During idle periods, a process called garbage collection ensures that old block information is erased, making the block available for rewriting. Another process known as TRIM informs the SSD that certain data can be skipped during block erasures, extending the drive’s lifespan. To prevent uneven wear on the drive, an algorithm ensures that each block receives an equal amount of read/write processes, known as wear leveling. SSDs are often overprovisioned with storage to allow for data movement and deletion without affecting the overall storage capacity.
Drawbacks of SSDs
Despite their benefits, SSDs are a more recent technology and are relatively more expensive than HDDs. While SSDs are catching up, it can still be challenging to find large-capacity SSDs. HDDs can offer up to 2.5 times more storage capacity than SSDs.
Benefits of SSDs
One of the most significant advantages of using an SSD is its remarkable speed compared to HDDs. If you’re wondering why you should choose a solid-state drive, consider this: SSDs offer faster load times for games, applications, and movies. Thanks to their advanced technology, Laptops with SSDs are not only faster but also lighter, making them more resistant to physical shocks and drops. Furthermore, SSDs are energy-efficient, allowing your computer to run cooler and consume less power.
HDD vs SSD – What’s Best for You?
In the modern era of computing, the primary drive in your PC should undoubtedly be an SSD. This means your operating system (OS) should run on an SSD, resulting in swift boot times, rapid application launches, and overall snappier performance. Even if you have budget constraints, consider investing in at least a 240 GB SSD to host the OS and key applications, while using an HDD for storing your larger data files.
Many modern laptops, particularly gaming laptops, come equipped with dedicated slots for both SSDs and HDDs, making it convenient to enjoy the best of both worlds. However, while choosing between HDD vs SSD, if budget concerns are not an issue, opting for an entirely SSD-based storage solution is the way to go. This not only ensures faster file access but also enhances your overall computing experience, as applications can tap into the stored data on the SSD at significantly higher speeds compared to traditional HDDs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between HDD vs SSD depends on your specific needs and budget. While HDDs may offer more storage at a lower cost, SSDs outshine them in terms of speed, durability, and efficiency. For a seamless and speedy computing experience, SSDs are the way forward, and incorporating them into your system, even if it means starting with a smaller capacity SSD, can significantly enhance your daily computing tasks. Whether you’re a gamer, professional, or casual user, the advantages of SSDs are hard to ignore in today’s technology-driven world. So, make the smart choice, and elevate your PC’s performance with a solid-state drive. Your computing experience will never be the same again!