
Introduction of Networking:
Creating a solid network infrastructure is crucial for businesses to ensure seamless communication and connectivity. The three essential components of networking — switches, routers, and wireless access points — play distinct roles in establishing a reliable network environment. Understanding their functions and benefits is key to setting up an efficient networking system.
1. Switches
Switches form the foundation of most business networks. Acting as controllers, switches connect devices like computers, printers, and servers within a building or campus network. By enabling communication between devices and facilitating resource sharing, switches enhance productivity and cost-efficiency.
There are two types of switches to consider:
a. Unmanaged switches: These switches require no configuration and are ideal for basic connectivity needs, commonly used in small office networks.
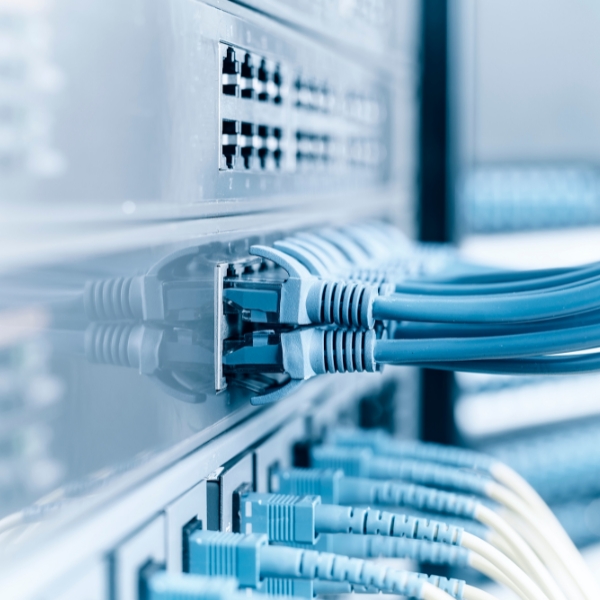

b. Managed switches: Offering greater control, security, and flexibility, managed switches allow customization to fit specific network requirements. They provide advanced features and enhanced quality of service, making them suitable for businesses that prioritize network performance and security.
Networking hubs are an older alternative to switches but come with limitations in terms of bandwidth and network congestion. Switches overcome these limitations and are the preferred choice for modern networks.
2. Routers
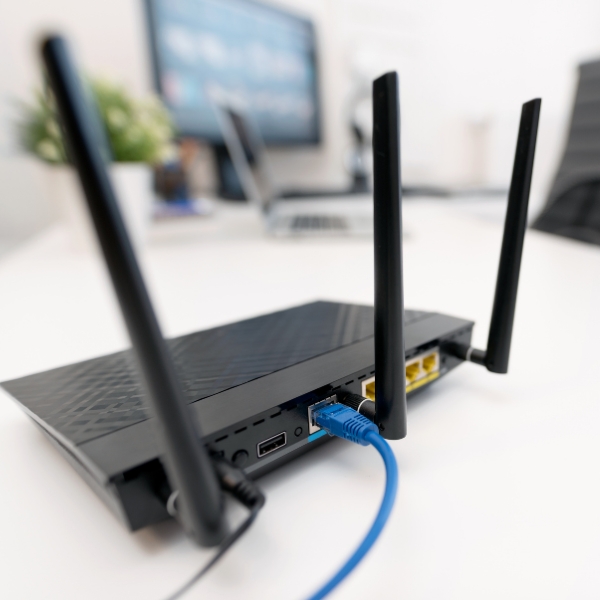
Routers connect multiple networks together, including computers within those networks to the Internet. They analyze data traffic, determine the best route for data transmission, and act as dispatchers within a network. Routers enable shared Internet access and provide security features like firewalls, VPNs, and IP communications systems.
In addition to basic networking functions, routers offer various advanced features to enhance network management, security, and performance. They play a crucial role in connecting businesses to the outside world and ensuring reliable data transmission.

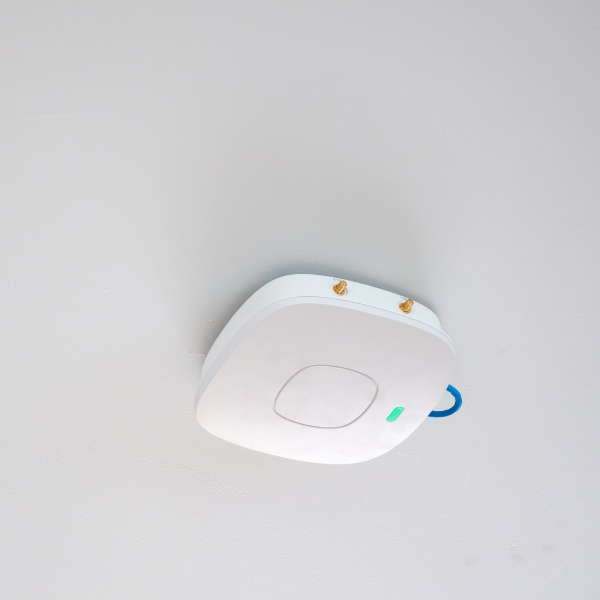
3. Access Points
Access points (APs) enable wireless connectivity by allowing devices to connect to a wireless network without cables. They amplify Wi-Fi signals, extending network coverage and providing flexibility for mobile workers. APs not only expand network reach but also provide valuable insights into connected devices and offer proactive security measures.
Wireless networks, powered by access points, offer the convenience of mobility and easy access to network resources. They have become an integral part of modern business environments, supporting productivity, collaboration, and ease of use.

Wireless Networks
A Wi-Fi wireless network allows devices to connect to the network without physical cables, providing flexibility and mobility. Access points amplify Wi-Fi signals, ensuring connectivity even at a distance from the router. In contrast, wired networks utilize cables to connect devices directly to the network or the Internet.
Wireless networks have evolved significantly, offering comparable speed and security to wired networks. The convenience, mobility, productivity, easy setup, expandability, and cost-effectiveness of wireless networks make them a popular choice for businesses.

Benefits of Wi-Fi wireless networks:
- Convenient access to network resources from any coverage area or Wi-Fi hotspot.
- Increased mobility and flexibility for employees to connect from various locations.
- Enhanced productivity and collaboration opportunities.
- Quick and cost-effective installation without the need for extensive wiring.
- Scalability and easy expansion using existing equipment.
- Robust security features to protect sensitive data.
- Potential cost savings by eliminating or reducing wiring expenses.
Internet Leased Line
An Internet leased line is a dedicated, fixed-bandwidth data connection directly from the Internet Service Provider that offers a secure, reliable, and highly efficient internet connection for businesses. It is a bidirectional telephone line that has been rented for private voice, data exchange, or telecommunication use. Leased lines are symmetrical, uncontended, and point-to-point connections, meaning they have equal upload and download speeds, are not shared with others, and connect two points, such as an ISP and a business location.
They are typically used by businesses to connect geographically distant offices and provide internet access, link computers and servers, and support remote access, large file transfers, data backup, voice over IP telephony, and hosting websites on premise. A leased line works by creating a constant tunnel between two points to enable a continuous data flow, and it is always active and rented monthly. It is a premium internet connectivity product delivered over fiber, providing uncontended, symmetrical bandwidth with full-duplex traffic.
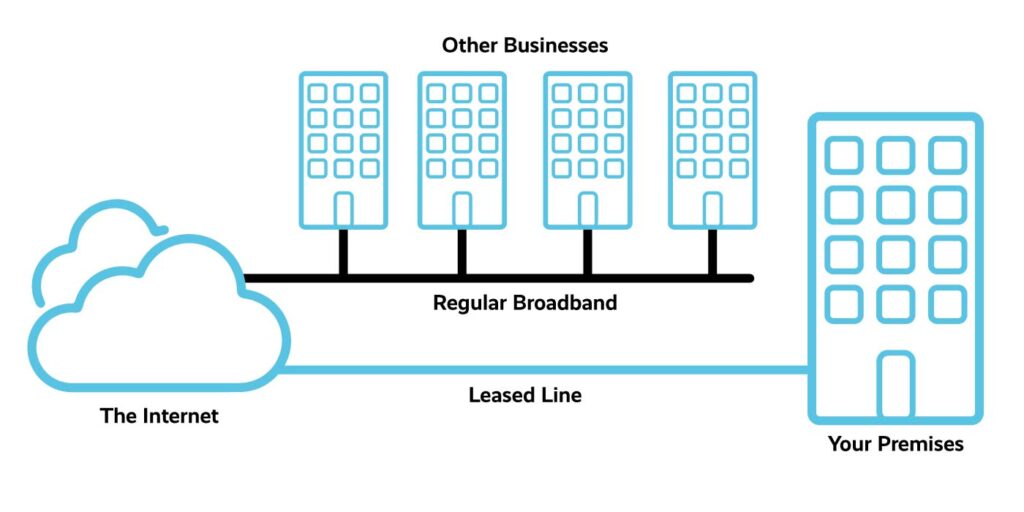
Leased Lines vs Broadband – Advantages of Internet Leased Line
- Speed : One of the significant advantages of leased lines lies in their provision of equally robust upload and download speeds. Broadband, while widely available, often grapples with inconsistent speeds, showcasing rapid download rates but considerably slower upload capacities.
- Reliability: When it comes to meeting promised speeds, leased lines triumph consistently. The dedicated nature of a leased line ensures you receive the full bandwidth capacity as advertised, a stark contrast to broadband connections that falter in delivering their advertised speeds due to shared bandwidth among multiple users.
- Latency: Ever experienced frustrating delays when actions like downloading critical documents or engaging in video conferences take longer than expected? These delays often stem from high latency, a prevalent issue with broadband connections. In contrast, leased lines offer low latency consistently, bypassing the frustrations associated with delayed responses. This low-latency consistency stems from a dedicated connection directly linking your business equipment to the Internet Service Provider’s (ISP’s) data center, ensuring swift interactions and seamless operations.
- Scalability and Control: As businesses evolve, their internet requirements tend to fluctuate. Leased lines provide the flexibility necessary for growth, enabling seamless adjustments in bandwidth to accommodate expanding needs. This scalability feature empowers businesses to ramp up or scale down services as needed, offering a level of control that’s notably advantageous.
- Leased Lines vs Regular Broadband: While regular broadband might suffice for smaller businesses with basic internet needs, a leased line proves indispensable for businesses reliant on seamless access to cloud-based systems, video-conferencing software, and other mission-critical online services.
- Reliability, SLAs and Downtime Mitigation: Leased line providers often back their services with robust Service Level Agreements (SLAs) ensuring guaranteed uptime and swift issue resolution. In contrast, most broadband providers lack comparable guarantees, potentially resulting in prolonged downtime during service interruptions.
Conclusion
Building a reliable Networking infrastructure requires careful consideration of switches, routers, and access points. Each component plays a vital role in establishing efficient connectivity, improving productivity, and ensuring seamless communication. If you’re uncertain about the networking setup that suits your business needs, don’t hesitate to reach out to us. Our experts can provide guidance and help you make informed decisions for your networking requirements.
Get in Touch
Nurture IT
50, 9th A Main Rd, Indira Nagar 1st Stage, Stage 1, Indiranagar, Bengaluru,
Karnataka 560038
Phone +91 9886349622
[email protected]
